|

You have worked with relations and functions in the past.
Let's refresh our memories and add a few more details.
|
|
A relation is simply a set of input and output values, represented in ordered pairs.
It is a relationship between sets of information. |
|
Any set of ordered pairs may be used in a relation.
No special rules need apply to a relation.
 |
Consider this example of a relation:
The relationship between eye color and student names.
(x,y) = (eye color, student's name)
Set A = {(green,Steve), (blue,Elaine), (brown,Kyle), (green,Marsha), (blue,Miranda), (brown, Dylan)}
Notice that the x-values (eye colors) get repeated. |
The scatter plot and the graph, shown below, are also examples of relations.
The thing to notice about them is that they also allow for one x-value
to have more than one corresponding y-value.
Points such as (1,1) and (1,2) can BOTH belong to the same relation.
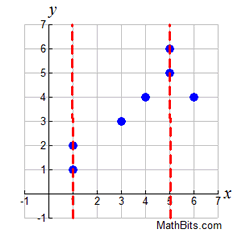 Relation:
Relation:
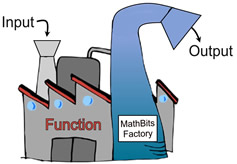
{(1,1),(1,2),(3,3),(4,4),(5,5),(5,6),(6,4)} |
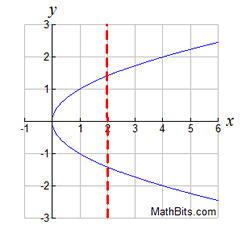 Relation:
Relation: 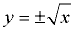 ; allows for points
such
as
(2,1.414) and (2,-1.414).
|
If you add a "specific rule" to a relation, you get a function.
|
A function is a set of ordered pairs in which each x-element has only ONE y-element associated with it.
|
|
 |
While a function may NOT have two y-values assigned to the same x-value,
it may have
two x-values assigned to the same y-value.
NOT OK for a function:
{(5,1),(5,4)} |
OK for a function:
{(5,2),(4,2)} |
Function: each x-value has only ONE y-value! |
Let's adjust our previous examples so they fit the function "definition".
If we remove duplicate eye colors,
the eye color example will be a function:
(x,y) = (eye color, student's name)
Set B =
{(blue,Steve), (green,Elaine), (brown,Kyle)}
Set B is a function. |
 |
And now the graphs:
If we remove (1,2) and (5,6),
we will have a function. 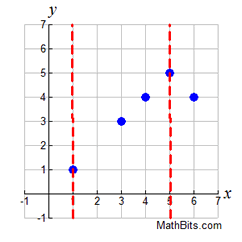 Function:
Function:
{(1,1),(3,3),(4,4),(5,5),(6,4)} |
If we change the ± sign to just a + sign,
we will have a function.
 Function:
Function: 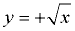
|
Notice that vertical lines on the graphs make it clear if an x-value had more than one y-value.
If the vertical lines intersected the graph in more than one location, we had a relation, NOT a function.
|
Vertical line test for functions: Any vertical line intersects the graph of a function in only ONE point. |
|

Given that relation A = {(4,3), (k,5), (7,-3), (3,2)}. Which of the following values for k will make relation A a function? a) 3 b) 4 c) 6
Solution: Choice c. The x-values of 3 and 4 are already used in relation A. If they are used again (with a different y-value), relation A will not be a function.

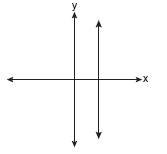
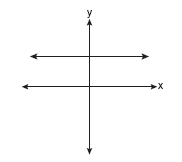
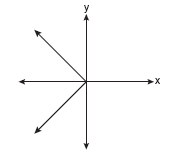
Which of the following graphs represents a function?
Solution: Choice b. A vertical line drawn on this graph will intersect the graph in only one location, making it a function. Vertical lines on the other three graphs will intersect the graph in more than one location, or as in part a, will intersect in an infinite number of points (all points).
|
Calculators graph functions! |
|
When you want to graph lines, you
1.
solve the equation for "y =", produce a chart of points (a T-chart), and plot, or
2.
solve the equation for "y =" plot the y-intercept and use slope to plot the line, or
3. solve the equation for "y ="
and enter the equation in your graphing calculator. |
By solving for "y =", you are actually identifying a "function".
If you can solve an equation for "y =", then the equation is a "function".
4x + 2y = 10
2y = -4x + 10
y = -2x + 5 (a function!)
This equation can now be entered into a graphing calculator for plotting.
Most calculators (including the TI-84+ series) can only handle graphing functions.
The equation (function) must be in "y = " form before you can enter it in the calculator.
BUT ... what about y2 = x ?
If we solve for "y =", we get 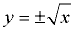 , which we saw, at top of this page, was not a function. , which we saw, at top of this page, was not a function.
We cannot graph this on our calculator as a single entity, since there is no key for "±".
We were not able to solve this equation for a unique (only one) "y =" equation.
We actually have two "y =" equations: 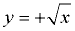 and and 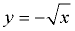 . .
(Yes, the graphing calculator can graph these equations separately to form the graph.
But the combined graphs will be a relation, not a function.)
The lack of a unique "y =" equation means that y2 = x is not a function.
NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet
is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |
|