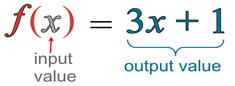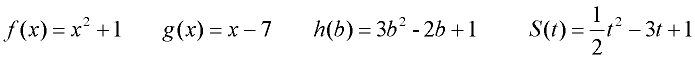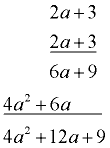|
Function notation is the way a function is written. It is meant to be a precise way of giving information about the function without a rather lengthy written explanation.
The most popular function notation is f (x) which is read "f of x".
This is NOT the multiplication of f times x.. |
|
|
Traditionally, functions are referred to by single letter names, such as f, g, h and so on.
Any letter(s), however, may be used to name a function. Examples:
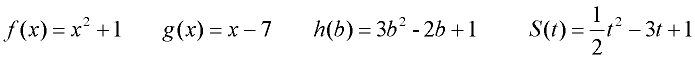 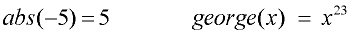
The f (x) notation is another way of representing the y-value in a function, y = f (x).
The y-axis may even be labeled as the f (x) axis, when graphing.
Ordered pairs may be written as (x, f (x)), instead of (x, y).
Note: The notation f : X → Y tells us that the function's name is "f " and its ordered pairs are formed by an element x from the set X, and by an element y from the set Y.
(The arrow → is read "is mapped to".)
|
Advantages of function notation:
1. |
it allows for individual function names to avoid confusion as to which function is being examined.
Names have different letters, such as f (x) and g (x).
The graphing calculator does distinctive function naming with Y1, Y2, ... |
2. |
it quickly identifies the independent variable in a problem. f (x) = x + 2b + c, where the variable is "x". |
3. |
it quickly states which element of the function is to be examined. Find f (2) when f (x) = 3x, is the same as saying, "Find y when x = 2, for y = 3x." |
|
Equivalent Notations! |
y = 3x + 2 |
f (x) = 3x + 2 |
f (x) = {(x,y) | y = 3x + 2}
(the vertical bar is read "such that") |
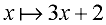 (the bar arrow means the element
(the bar arrow means the element
"x is mapped/matched to 3x + 2") |
|
|
| |
 |
|
To evaluate a function, substitute the input (the given number or expression) for the function's variable (place holder, x).
Replace the x with the number or expression.
|
1. |
Given the function f (x) = 3x - 5, find f (4).
Solution: Substitute 4 into the function in place of x. f (4) = 3(4) - 5 = 7.
This answer can be thought of as the ordered pair (4,7).
The answer may also be referred to as the image of 4 under f (x). |
2. |
Find the value of h (b) = 3b2 - 2b + 1 when b = -3.
Solution: Substitute -3 into the function in place of b. h (-3) = 3(-3)2 - 2(-3) + 1 = 34.
|
3. |
Find g (2w) when g (x) = x2 - 2x + 1.
Solution: When substituting expressions, like 2w, into a function, using parentheses will help prevent algebraic errors. For this problem, use (2w).
g (2w) = (2w)2 - 2(2w) + 1 = 4w2- 4w +1 (Note: the answer is in terms of w.) |
4. |
Given f (x) = 2x2 + 4x - 3, find f (2a + 3).
Solution: Be sure to use parentheses!
Be careful - more algebra work is needed here.
f (2a + 3) = 2(2a + 3)2 + 4(2a + 3) - 3
= 2(4a2 + 12a + 9) + 8a + 12 - 3
= 8a2 + 24a + 18 + 8a + 12 - 3
=
8a2 + 32a + 27 |
Did you multiply?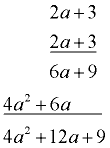 |
|
|
5. |
Given f (x) = x2 - x - 4. If f (k) = 8, what is the value of k?
Solution: Set the function rule equal to 8 and solve for k.
x2 - x - 4 = 8
x2 - x - 12 = 0
(x - 4)(x + 3) = 0
x - 4 = 0; x + 3 = 0
x = 4; x = -3 |
The value of k can be either 4 or -3. |
|
|
For calculator help with
evaluating expressions and functions
click here. |
|

NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet
is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |
|