Solid geometry is the geometry of three-dimensional space.
It is the study of properties, surface area, and volume of three-dimensional shapes.
It is of particular importance since we live in a three-dimensional world.
A geometric solid is a shape that has three-diminsions, occupies space, and has volume.
More formally, a geometric solid is a portion of space which is completely enclosed, or separated from the rest of space, by some type of surface.
There are two types of geometric solids: "polyhedrons" and "non-polyhedrons".
Remember: A polygon is a 2-dimensional closed figure that is the union of line segments in a plane. A polygon has three or more sides. There are no curved lines or segments.
|
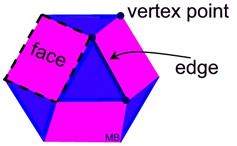
A polyhedron (plural polyhedrons or polyhedra) is a three-dimensional solid with flat polygon faces joined at their edges.
Each face is a polygon. |
|
The word polyhedron is derived from the Greek poly meaning "many",
and the Indo-European hedron meaning "seat or face".
|
A polyhedron has no curved surfaces.
The "faces" are the flat, plane surfaces.
The "edges" are the segments of intersection of the faces.
The "vertices" are the intersections of the edges (corner points).
|
Not ALL Faces are Congruent:
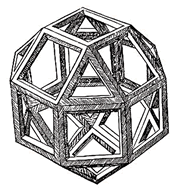
Polyhedra are not necessarily constructed using the same shaped polygons for faces. The skeletal polyhedron at the right, and the one shown above, are examples where the faces have varying numbers of sides. The example at the right is called a rhombicuboctahedron, and was drawn by Leonardo da Vinci as an illustration in a book. |
 |
Leonhard Euler (1701-1783) discovered that the number of vertices, V, (corner points)
of a polyhedron
minus the number of edges, E,
plus the number of faces, F, (flat surfaces) equals 2.
Euler's Polyhedral Formula: V - E + F = 2 |
Let's test Euler's Formula on a CUBE:
• V = 8 vertices (corner points)
• E = 12 edges
• F = 6 faces
V - E + F = 8 - 12 + 6 = 2 |
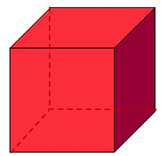 All faces are squares.
All faces are squares. |
Types of Polyhedrons:
We will be examining various types of prisms and pyramids, along with "regular" polyhedrons.
A polyhedron is "regular" if its faces are congruent, regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. There are a total of five such convex regular polyhedrons called the Platonic Solids, after the ancient Greek philosopher Plato, in whose writings they first appeared.
Platonic Solids
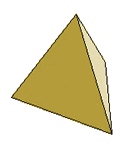
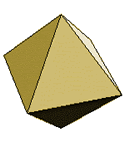
Tetrahedron |
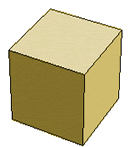
Cube |
Octahedron |
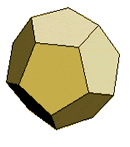
Dodecahedron |
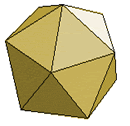
Icosahedron |
|
|
|
|
|
4 faces
equilateral triangles |
6 faces
squares |
8 faces
equilateral triangles |
12 faces
regular pentaton |
20 faces
equilateral triangles |
The cube is also called a hexahedron.
With the use of Euler's formula, it was discovered that there are ONLY five different regular convex polyhedrons. While there is no limit to the number of regular polygons, there is a limit to the number of regular polyhedrons! There are only five!
Read more about Platonic Solids.
Tidbits of Info:
|
A soccer ball is composed of a combination of 12 pentagon and 20 hexagon faces. The shape of a soccer ball may be compared to that of a "buckyball", named after Richard Buckminster Fuller, who patented the geodesic dome. In reality, the soccer ball is not truly a polyhedron since the faces are not really flat. The faces tend to bulge slightly due to the amount of compressed air in the ball and the pliable nature of the leather. |
[A buckyball is actually a spherical molecule whose structure resembles a truncated icosahedron with 20 hexagons and 12 pentagons.]
|
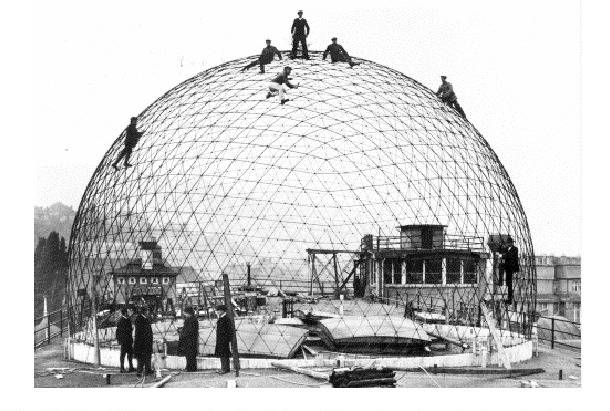

A geodesic dome designed for a planetarium. |
A geodesic dome is a triangulation of a Platonic solid to approximate a sphere. The idea was patented by Richard Buckminster Fuller, an American architect. It is constructed of interlocking equilateral triangles.
A geodesic dome can withstand very heavy loads for their size, as the triangular components of the dome distribute stress throughout the structure.
|
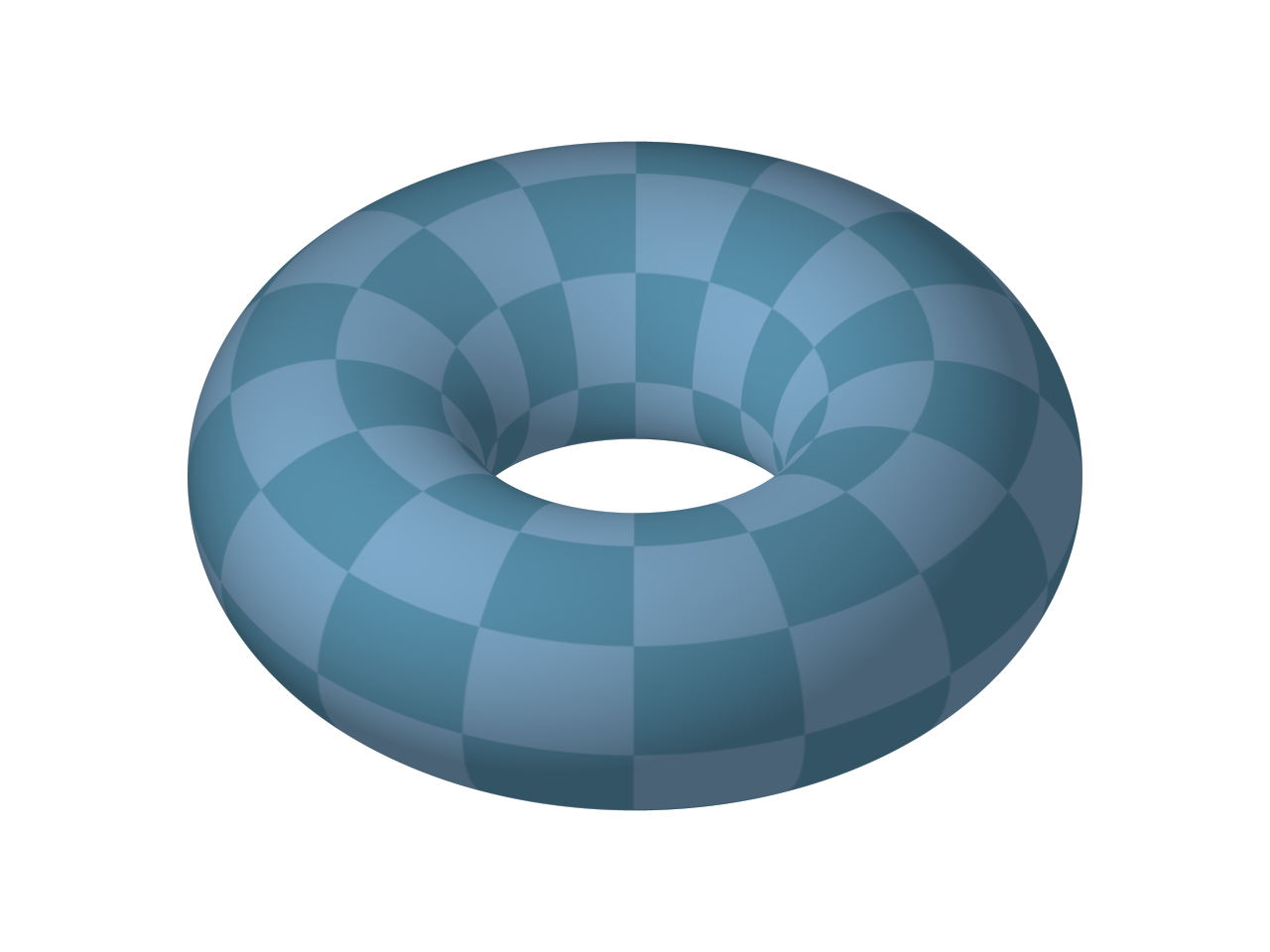
The following solids are NOT polyhedrons since a part, or all, of the figure is curved.
Cylinder |
Cone |
Sphere |
Torus |
|
|
|
|
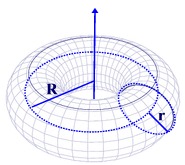
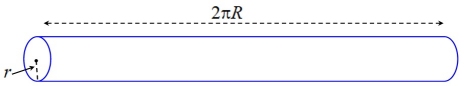
A "torus" is a "tube shape". It is the result of revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface is a ring shape (with a hole in the middle). Examples include an inner tube, a dough-nut, a tire, and a bagel.
You can think of a torus as revolving a smaller circle about a larger circle. |
|
In the diagram at the left, small r is the radius of the tube and capital R is the distance from the center of revolution of the torus to the center of the tube.
If the torus has a hole in the center:
the Surface Area: SA = (2πR) (2πr) = 4π2
Rr
the Volume: V = (2πR)(πr2) = 2π2 Rr2
|