|
Directions: Read carefully.
1. |
Two vertical angles are expressed as
(½)x + 12 and (¾)x + 8.
Find the value of x.
Choose:
|
 |
|
2. |
Two complementary angles are expressed as
4x - 16 and 2x + 10. Find the number of degrees in each angle.
Choose:
|
|
|
3. |
∠ABD and ∠CBD form a linear pair.
If m∠ABD = 6x - 12 and m∠CBD = x + 31,
find the m∠ABD.
Choose:
|
|
|
4. |
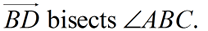
m∠ABD = 2.5x + 8.6
m∠CBD = 3.5x - 3.4
Find m∠ABCChoose:
|
|
|
5. |
As seen in the diagram at the right:
m∠RSW = 2x + 16; m∠WSV = 3x + 2
m∠UST = 2x; m∠VSU = m∠UST
Find m∠WSV.
Choose:
|
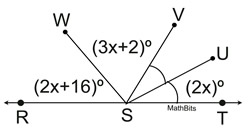
straight <RST |
|
6. |
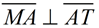 The angles are represented as shown.
The angles are represented as shown.
Find m∠HAT
Choose:
|
|
|
7. |
Diagram as shown and labeled.
a) Find x.
Choose:
b) Find m∠CMD.
Choose:
|
|
|
8. |
intersecting at H.
Find x and y.
Choose:
|
|
|
9. |
The ratio of m∠CBE to m∠DBE to m∠ABD is 1 : 2 : 3 as shown.
∠ABC is a straight angle.
Find m∠DBE. Choose:
|
|
|
|
10. |
In the diagram at the right,
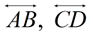
and angles are labeled.
Find m∠AED.
|
|
|

NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet
is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |
|