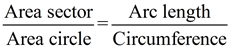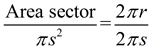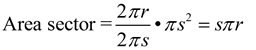Volume of a Cone (for both right and oblique cones):
The volume of a cone is one-third the area of its base times its height. 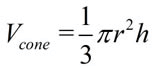 |
|
The formula for the volume of a cone is very similar to the formula for the volume of a pyramid, 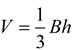 . Note: A cone is not a pyramid since its base is circular (not a polygon).
The volume of a cone is one-third of the base area, πr2, times the height of the cone.
|
Since the base of a cone is a circle, you can see how replacing the B value in the volume of the pyramid with the area of a circle gives us the volume formula for a cone.
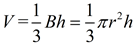 |
|
V = volume in cubic units
r = radius of base in units
h = height in units
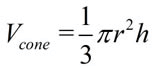
|
Also notice that the volume of a cone is one-third the volume of a cylinder with the same base and height.
Example:
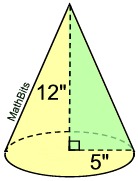
Find the volume of this right circular cone, to the nearest tenth of a cubic inch.
Solution:
• The radius = 5 inches.
• The height = 12 inches.
• The volume formula is:
 |
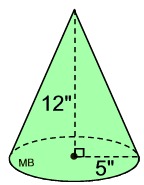 Note: The slant height of this cone will be 13 inches, from the
Note: The slant height of this cone will be 13 inches, from the
5-12-13 right triangle. |
|
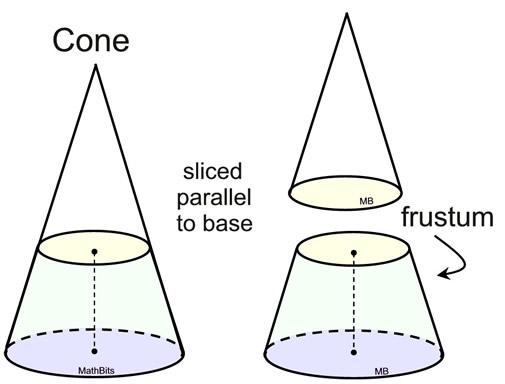
Justification of formula by "comparison to pyramid":
For this comparison, we need to have solids whose bases have equal areas and whose cross sections parallel to the bases have equal areas.
(We will be applying Cavalieri's Principle that will show these figures have the same volume.)
Can we find a way to have bases of equal area on a right circular cone and a regular square pyramid?
The area of the circular base of the cone is πr2.
The area of the base of the square pyramid is s2.
If these two areas are equal, we must have πr2 = s2.
Solving for s, tells us that the side of the square base must have a length of 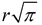 .
.
Now, the circular base and the square base have the same area. If we can establish that cross sections parallel to the bases yield the same areas, we will be show that the volumes are equal.
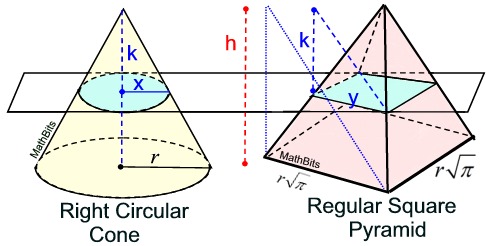
Let's say that our cross section is drawn k units down from the top of both solids.
By similar triangles, we know the proportion x / r = k / h, and x = (r)•(k / h).
In the cone, with a radius x = (r)•(k / h), the area of the circular cross section is
πx2 = π[(r)•(k / h)]2.
In the pyramid, we know the proportion y /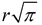 = k / h, which gives length y =
= k / h, which gives length y = 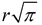 • (k / h).
• (k / h).
The area of the cross section in the pyramid =
[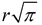 • (k / h) ]2.
• (k / h) ]2.
Now, π[(r)•(k / h)]2 = π • r2 • (k / h)2.
And, [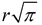 • (k / h) ]2 = π • r2 • (k / h)2.
• (k / h) ]2 = π • r2 • (k / h)2.
Since the cross sectional areas are also equal, we can employ Cavalieri's principle and state that the volume of the cone equals the volume of the pyramid. We know that the volume of the pyramid is 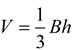 . Since the height is the same in both solids, and B must equal πr2 for the cone, we have that the formula for the volume of a cone
. Since the height is the same in both solids, and B must equal πr2 for the cone, we have that the formula for the volume of a cone 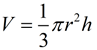 .
.
Surface Area of a Cone:
|
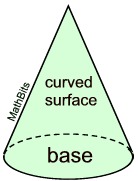
The surface area of a closed right cone is a combination of the lateral area and the area of the base. |
|
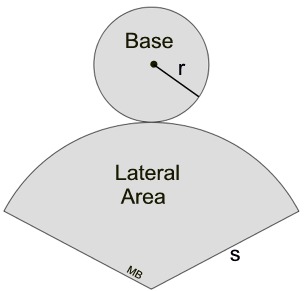
When cut along the slant side and laid flat, the surface of a cone becomes one circular base and the sector of a circle (lateral surface), as seen in the net at the right.
The length of the arc in the sector is the same as the circumference of the small circular base.
Remember that the area of a sector is a portion of the area of a complete circle. With this in mind, we can use proportions to find the area of a sector.
|
|
|
These calculations refer to the "sector" section of the cone's net. |
|
The arc length of the sector equals the circumference of the base circle. |
|
The radius of the base circle is r, while the radius of the sector is s. |
The base area = area of a circle = πr2.
The lateral area (sector) = sπr.
Note: The area of the sector is half the product of the slant height and the circumference of the base. sπr = ½ s • 2πr
|
Total Surface Area of a Closed Cone
SA = sπr + πr2
SA = surface area
r = radius of the base
s = slant height of the cone |
|
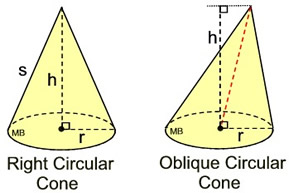
In a right circular cone, the slant height, s, can be found using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Create a right triangle using the height, the radius and the slant height.
s2 = r2 + h2
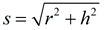 |
 |
|
When asked to find the surface area of a cone, be sure to read the question carefully.
|
Will the surface area
include the base?
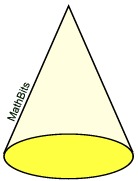
SA = sπr + πr2
|
Will the surface area
NOT include the base?
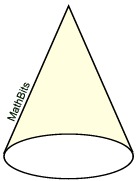
SA = sπr |
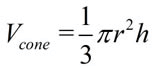
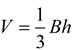 . Note: A cone is not a pyramid since its base is circular (not a polygon).
. Note: A cone is not a pyramid since its base is circular (not a polygon). 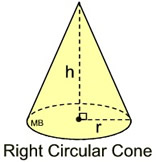



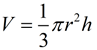 .
.