|
If you can solve a linear equation, you can solve a linear inequality. The process is the same, with one exception ...
|
... when you multiply (or divide) an inequality by a negative value,
you must change the direction of the inequality. |
 |
While you should be aware of the exception mentioned above, this web page on one-step inequalities will NOT be multiplying or dividing by negative values. |
Let's compare solving an equation with solving an inequality:
The process of adding or subtracting to solve for the variable x is the same when solving equations and inequalities.
Equation: Solve for x:
x + 3 = 5
Solution: Subtract 3 from both sides.
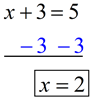 |
Inequality: Solve for x:
x + 3 < 5
Solution: Subtract 3 from both sides.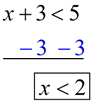
|
The process of multiplying or dividing to solve for the variable x is the same when solving equations and inequalities, for multiplying or dividing by a positive value.
(The "exception" stated above would come into play if multiplying or dividing by a negative value.)
Equation: Solve for x:
5 x = 35
Solution: Divide both sides by 5.
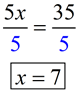 |
Inequality: Solve for x:
5 x > 35
Solution: Divide both sides by 5.
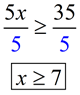
|
Solve for x: 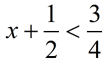
|
|
Solve for x: 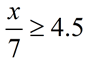
|
|
Given the inequality, 8x < 24, which choice represents the values that will make this inequality true?
A x > 3 B x < 3 C x < 16 D x > -3
|
|

What number is not part of the solution set to the inequality b - 12 < 23?
A 18 B 24 C 34 D 36
|
|